Internal pipe insulation technology - coating materials and properties of the protective layer
There are three types of protective layers applied inside pipelines transporting liquid or gaseous media (depending on the purpose). The first type includes anti-corrosion internal insulation of steel pipes, the second - a smooth coating. The third option is a complex structure that enhances the pipeline’s resistance to mechanical stress.
The content of the article:
The history of the creation of this kind of insulation
Until the mid-70s of the 19th century, treatment of the inner surface of metal pipes was carried out by CPI (cement-sand insulation). Insulation technology paints and varnishes based on epoxy resins first tested at the Volzhsky TZ. Since 1975, at a recently (1970) launched enterprise, a workshop for applying an external anti-corrosion layer has been put into operation. In the first year of operation, over a million units of products were produced.
The enterprise carried out complete external and internal insulation of steel pipes with a diameter of 53-142 cm. Production tasks were solved in partnership with the Yaroslavl paint and varnish plant, from where powdered materials were supplied.
Apart from Russia, the technology of epoxy insulation of metal pipes remains the main one in:
- Asia (India, China);
- North America (USA, Canada);
- in southern Africa (South Africa).
Alternative materials for anti-corrosion protection are polymers (PE, PP, PU), silicate-enamel mixture, and other two-component compositions.
Types of factory-made epoxy insulation
The classification of protective coatings for pipelines is carried out according to their composition, number of layers and method of application. The process of “liquid” internal insulation of steel pipes is characterized by simple technology. Polymerization of the composition occurs at 60-70 ° C for several hours.
When spraying the powder composition, additional heating of the surface to 190-210 °C is required. Polymerization ultimately takes longer. Arguments in favor of powder technology:
- higher productivity;
- wider range of modifications in relation to the transported medium;
- safer for the environment.
The choice between “liquid” and powder methods is relevant for new enterprises. The remaining factories operate using technology for which they already have equipment installed.
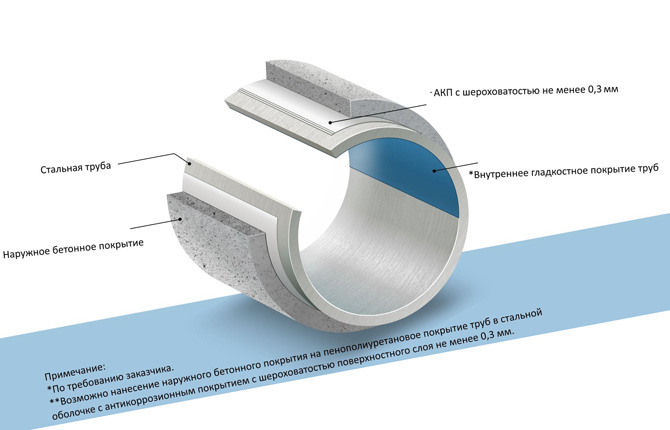
Internal insulation structure
Epoxy and complex coatings are applied to metal pipes in 1-3 layers. The weld zone on the inner surface is processed separately. It is closed with a steel coupling protected by an epoxy layer on both sides.
The structure of internal insulation affects the technical parameters, service life and scope of operation of the future highway:
- Single coating is suitable for small and medium diameter pipes. The scope of application of the products is limited by the temperature of the working environment - not higher than 80 °C.
- Two layers. The insulation is formed from an anti-corrosion (320 microns) and protective (440-750 microns) coating. It has increased resistance to impacts and aggressive environments (by 31%) and reduces surface roughness by 16%. Operation in “hot” areas (above 80 °C) is allowed.
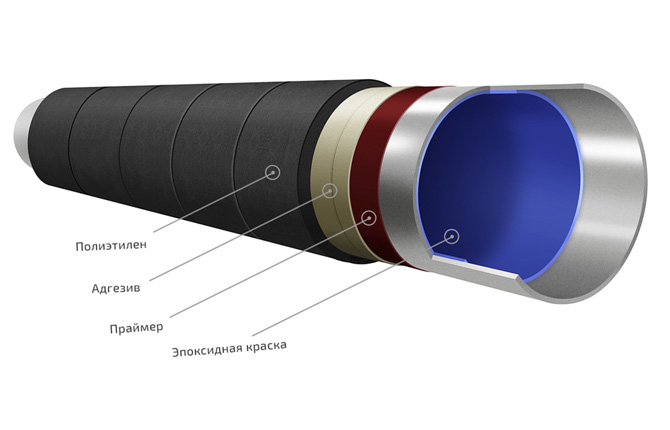
- Triplex. The epoxy “primer” is complemented by two polyethylene layers. It is characterized by durability and increased adhesion.
The technology for forming a combined coating was developed by Simitomo Metal Ind. First, a complex composition of various resins is applied. The thickness of the “base” is 100-300 microns.
The structure is dominated by epoxy resin, which has high adhesion to metals and PE polymers. The porous surface of the base increases adhesion to the steel and subsequent layers of internal pipe insulation. The further applied polymer structures are resistant to most acids and increase the degree of protection against mechanical damage.
Positive properties of epoxy insulation
Pipelines with an internal protective coating have increased throughput and service life. Another important point is that the cost of their annual maintenance is reduced.
Direct internal insulation of steel pipes helps reduce crystallization and wax deposition. The total cost of cleaning the highway is reduced by 54-75%. The exact figure depends on the type of distillation medium.
Other advantages of epoxy insulation:
- high heat resistance increases the operating temperature limit to 80 °C, with a certain composition – up to 110 °C;
- the composition and quality of transported substances is preserved;
- increased resistance to cathodic disbonding – no cases of stress corrosion have been recorded;
- energy costs are reduced due to a decrease in the roughness of the internal surface;
- pipeline installation time is reduced - the epoxy layer requires less time to dry after test runs;
- compliance with environmental standards - the insulation does not contain coal tar;
- the formation of mineral deposits is eliminated - failure of valves and other shut-off valves is minimized;
- The steel walls of the pipeline do not corrode, which increases the service life.
The last point is especially important when transporting aggressive substances. The rate of general corrosion is 0.01-0.4 mm/year. The local indicator is even higher – 6 mm/year.
The epoxy compounds used do not contain toxic resins or other substances hazardous to human health. In addition, x application prevents the formation of colonies of microorganisms. The listed properties allow the use of pipelines for supplying drinking water and in the food industry.
The disadvantage of epoxy technology is its low impact strength. Therefore, pipes with single-layer insulation require special attention during installation and transportation.
Features of CPI coating
Cement-sand insulation initially provides resistance to mechanical damage and shock. Chemical protection is activated the first time the transported substance passes through the highway. The fluid flow affects the CPI. The smallest grains of insulation are pressed and spread over the steel surface, filling the pores on the walls of the pipeline. The process is accompanied by the formation of calcium hydroxide, which completely suppresses corrosion.
The thickness of the insulating layer is 4-16 mm along the length of the pipe and from 3 mm at the welds. The compressive strength of the CPI coating is not lower than 445 MPa. The only sources of metal destruction are aging and mechanical damage.
Conclusion
Internal anti-corrosion insulation of steel pipes is carried out with a cement-sand composition, polymer or paint coatings based on epoxy resins. The procedure ensures high quality of transported substances at the delivery point.The service life of the highway is increased and maintenance costs are reduced.
The applied coatings prevent the formation of mineral, biological and paraffin deposits. This expands the scope of use of pipelines and saves energy consumption.
How effective do you think is the use of epoxy compounds for internal pipe insulation? Write in the comments. Share the article on social networks and save it to bookmarks.
Epoxy insulation on the inner surface of pipes in the video.