Do-it-yourself time relay: review of 3 homemade options
You can activate and deactivate household appliances without the presence and participation of the user. Most models produced these days are equipped with a time relay for automatic start/stop.
What to do if you want to manage outdated equipment in the same way? Be patient, take our advice and make a time relay with your own hands - believe me, this homemade product will find application in the household.
We are ready to help you implement an interesting idea and try your hand at becoming an independent electrical engineer. For you, we have found and systematized all the valuable information about the options and methods of making relays. Using the information provided will ensure easy assembly and excellent performance of the device.
The article proposed for study examines in detail the self-made versions of the device that have been tested in practice. The information is based on the experience of craftsmen passionate about electrical engineering and the requirements of regulations.
The content of the article:
Scope of application of time relay
Man has always sought to make his life easier by introducing various devices into everyday life. With the advent of electric motor-based equipment, the question arose about equipping it with a timer that would control this equipment automatically.
Turn it on for a specified time - and you can go do other things. The unit will switch itself off after the set period. For such automation, a relay with an auto-timer function was required.
A classic example of the device in question is in a relay in an old Soviet-style washing machine. On its body there was a handle with several divisions. I set the desired mode, and the drum spins for 5–10 minutes until the clock inside reaches zero.

Today time relay installed in various equipment:
- microwaves, ovens and other household appliances;
- exhaust fans;
- automatic watering systems;
- automatic lighting control.
In most cases, the device is made on the basis of a microcontroller, which simultaneously controls all other operating modes of automated equipment. It's cheaper for the manufacturer. There is no need to spend money on several separate devices responsible for one thing.
Based on the type of element at the output, time relays are classified into three types:
- relay - the load is connected via a “dry contact”;
- triac;
- thyristor.
The first option is the most reliable and resistant to network surges. A device with a switching thyristor at the output should be used only if the connected load is insensitive to the shape of the supply voltage.
To make your own time relay, you can also use a microcontroller. However, homemade products are mainly made for simple things and work conditions. An expensive programmable controller in such a situation is a waste of money.
There are much simpler and cheaper circuits based on transistors and capacitors. Moreover, there are several options; there is plenty to choose from for your specific needs.
Schemes of various homemade products
All proposed options for making time relays with your own hands are based on the principle of starting a set shutter speed. First, a timer is started with a specified time interval and countdown.
The external device connected to it begins to work - the electric motor or light turns on.And then, when zero is reached, the relay issues a signal to turn off this load or cuts off the current.
Option #1: the simplest with transistors
Transistor-based circuits are the easiest to implement. The simplest of them includes only eight elements. You don’t even need a board to connect them; everything can be soldered without it. A similar relay is often made to connect lighting through it. I pressed the button and the light stayed on for a couple of minutes and then turned itself off.
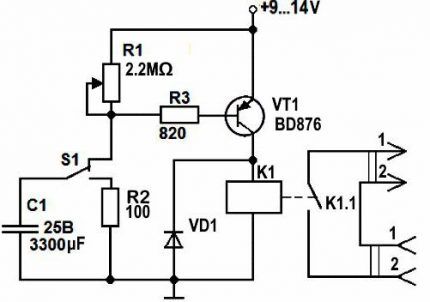
To assemble this homemade time relay, you will need:
- a pair of resistors (100 Ohm and 2.2 mOhm);
- bipolar transistor KT937A (or analogue);
- load switching relay;
- 820 Ohm variable resistor (to adjust the time interval);
- capacitor 3300 µF and 25 V;
- rectifier diode KD105B;
- switch to start counting.
The time delay in this timer relay occurs due to the charging of the capacitor to the power level of the transistor switch. While C1 is charging to 9–12 V, the key in VT1 remains open. The external load is powered (light is on).
After some time, which depends on the set value on R1, transistor VT1 closes. Relay K1 is eventually de-energized and the load is disconnected from voltage.
The charging time of capacitor C1 is determined by the product of its capacitance and the total resistance of the charging circuit (R1 and R2). Moreover, the first of these resistances is fixed, and the second is adjustable to set a specific interval.
The timing parameters for the assembled relay are selected experimentally by setting different values on R1.To make it easier to set the required time later, markings with minute positioning should be made on the housing.
Specifying a formula for calculating the output delays for such a scheme is problematic. Much depends on the parameters of a particular transistor and other elements.
The relay is brought to its original position by switching S1 back. The capacitor closes to R2 and discharges. After S1 is switched on again, the cycle starts again.
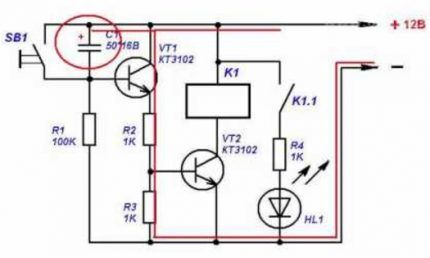
In a circuit with two transistors, the first one is involved in the regulation and control of the time pause. And the second is an electronic key for turning on and off the power to the external load.
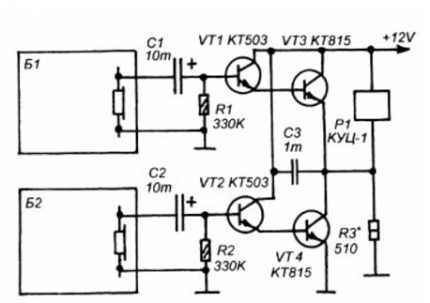
The most difficult thing in this modification is to accurately select the resistance R3. It should be such that the relay closes only when a signal is supplied from B2. In this case, the reverse switching on of the load must occur only when B1 is triggered. It will have to be selected experimentally.
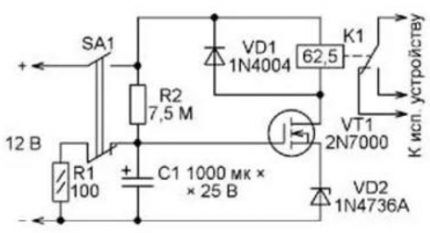
This type of transistor has very low gate current. If the resistance winding in the control relay switch is selected to be large (tens of Ohms and MOhms), then the shutdown interval can be increased to several hours. Moreover, most of the time the timer relay consumes virtually no energy.
The active mode in it begins at the last third of this interval. If the radio is connected via a regular battery, it will last a very long time.
Option #2: chip-based
Transistor circuits have two main disadvantages. It is difficult to calculate the delay time for them and the capacitor must be discharged before the next start. The use of microcircuits eliminates these disadvantages, but complicates the device.
However, if you have even minimal skills and knowledge in electrical engineering, making such a time relay with your own hands is also not difficult.
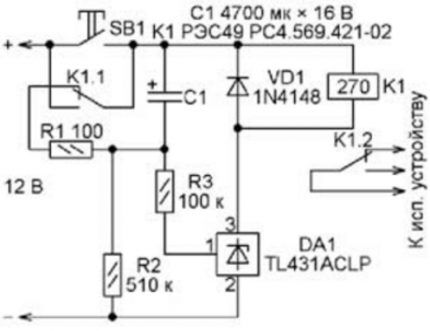
The opening threshold of the TL431 is more stable due to the presence of a reference voltage source inside. Plus, switching it requires a much higher voltage. At the maximum, by increasing the value of R2, it can be raised to 30 V.
The capacitor will take a long time to charge to such values. In addition, connecting C1 to the resistance for discharge in this case occurs automatically. There is no need to additionally press SB1 here.
Another option is to use the NE555 “integral timer”. In this case, the delay is also determined by the parameters of the two resistances (R2 and R4) and the capacitor (C1).
The relay is “turned off” by switching the transistor again. Only its closing here is carried out by a signal from the output of the microcircuit, when it counts down the required seconds.
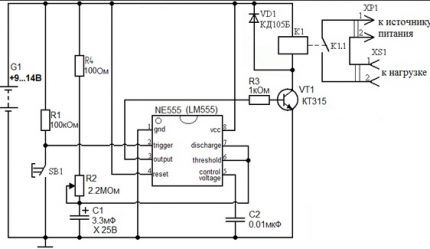
There are much fewer false positives when using microcircuits than when using transistors. In this case, the currents are more tightly controlled, the transistor opens and closes exactly when required.
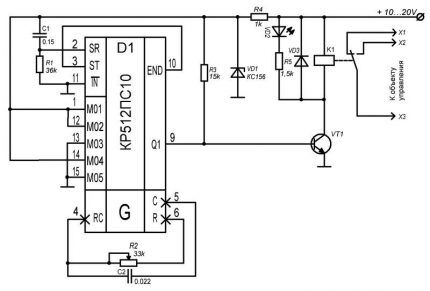
Another classic microcircuit version of the time relay is based on the KR512PS10. In this case, when the power is turned on, the R1C1 circuit supplies a reset pulse to the input of the microcircuit, after which the internal oscillator starts in it. The shutdown frequency (division factor) of the latter is set by the regulating circuit R2C2.
The number of counted pulses is determined by switching the five pins M01–M05 in various combinations. The delay time can be set from 3 seconds to 30 hours.
After counting the specified number of pulses, the output of the Q1 microcircuit is set to a high level, opening VT1. As a result, relay K1 is triggered and turns the load on or off.
There are even more complex time relay circuits based on microcontrollers. However, they are not suitable for self-assembly. This is where difficulties arise with both soldering and programming. Variations with transistors and simple microcircuits for domestic use are quite enough in the vast majority of cases.
Option #3: for power supply at 220 V output
All of the above circuits are designed for a 12-volt output voltage. To connect a powerful load to a time relay assembled on their basis, it is necessary at the output install a magnetic starter. To control electric motors or other complex electrical equipment with increased power, you will have to do this.
However, to regulate household lighting, you can assemble a relay based on a diode bridge and a thyristor. However, it is not recommended to connect anything else through such a timer.The thyristor passes through itself only the positive part of the sine wave of 220 Volt variables.
This is not a problem for an incandescent light bulb, fan or heating element, but other electrical equipment may not be able to withstand this and burn out.
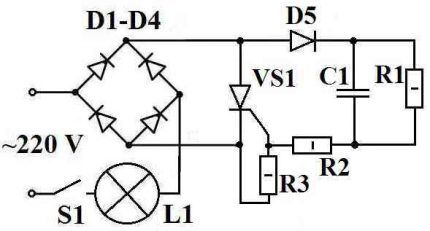
To assemble such a timer for a light bulb you need:
- resistances are constant at 4.3 MOhm (R1) and 200 Ohm (R2) plus adjustable at 1.5 kOhm (R3);
- four diodes with a maximum current above 1 A and a reverse voltage of 400 V;
- 0.47 µF capacitor;
- thyristor VT151 or similar;
- switch.
This relay-timer operates according to the general scheme for similar devices, with gradual charging of the capacitor. When contacts are closed on S1, C1 begins to charge.
During this process, thyristor VS1 remains open. As a result, the load L1 receives a mains voltage of 220 V. After charging C1 is completed, the thyristor closes and cuts off the current, turning off the lamp.
The delay is adjusted by setting the value on R3 and selecting the capacitance of the capacitor. It must be remembered that any touch to the bare legs of all used elements may result in electric shock. They are all powered by 220 V.
If you don’t want to experiment and assemble a time relay yourself, you can choose ready-made options for switches and sockets with a timer.
More details about such devices are written in the articles:
- Switch with shutdown timer: how it works and which type is better to choose
- Socket with timer: types, principle of operation + installation features
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Understanding the internal structure of a time relay from scratch is often difficult. Some lack knowledge, while others lack experience. To make it easier for you to choose the right circuit, we have made a selection of videos that detail all the nuances of the operation and assembly of the electronic device in question.
The operating principle of time relay elements on a transistor switch:
Automatic timer on a field-effect transistor for a 220 V load:
Step-by-step manufacturing of a delay relay with your own hands:
Assembling a time relay yourself is not too difficult - there are several schemes for implementing this idea. All of them are based on the gradual charging of a capacitor and the opening/closing of a transistor or thyristor at the output.
If you need a simple device, then it is better to take a transistor circuit. But to accurately control the delay time, you will have to solder one of the options on one or another microcircuit.
If you have experience assembling such a device, please share the information with our readers. Leave comments, attach photos of your homemade products and participate in discussions. The communication block is located below.




Interesting. Tell me, is it possible to connect the boiler through a relay for 220 volt power? Is there a heating element there? And if I understand correctly, then the boiler should not fail due to the fact that only the positive part of the voltage passes through? And by the way, are you planning to release a guide on how to make a book-lamp with your own hands? I saw several diagrams on the Internet, but they are not very clear. And everything is written in detail and clearly.
Good afternoon, Ilya.The article contains a section “Option #3: for 220 V output power,” which begins with the words: “All of the above circuits are designed for a 12-volt output voltage. To connect a powerful load to a time relay assembled on their basis, it is necessary to install a magnetic starter at the output.” In other words, no one includes heating elements in the devices listed before this section.
Taking into account the wording of your questions, I advise you to purchase a ready-made socket timer - the simplest 16-amp TRM-01 (daily operation time setting - time setting step 30 minutes) costs 240 rubles. Externally similar electronic one for 500 rubles. – TRE-01 for the same amperes – has expanded capabilities (weekly schedule, setting step – 1 min.)
Regarding the “book-lamp”, everything is simple: to prevent the pages from catching fire, you need to use an LED lamp powered by a battery. There is nothing complicated - it’s a shame to spoil books.
Good afternoon, Ilya. The boiler can be connected to 220V. You just need to select the diode bridge and thyristor in accordance with the power of the heating element. It’s just that you won’t be able to turn on a boiler for a long time with these component ratings.