Internet cable: types, device + what to look for when buying an Internet cable
Both to connect a computer and to create a network, you need an Internet cable.Although this is a passive component, it is no less important than the other elements.
To ensure that an incorrectly selected conductor does not damage the equipment, you need to become familiar with the types of cables, their features and purpose. We will talk about all this in detail in our article. We also provide a list of characteristics that you should first look at when choosing a suitable cable.
The content of the article:
Main types of cables for the Internet
In order to increase the speed of data transfer in local networks, the requirements of standards for transmission cables are becoming more and more complex. Internet cables differ from one another in different characteristics.
Let's look at the main types of these products:
- twisted pair;
- fiber optic;
- coaxial.
In addition to the cable category, important points are: core type, shielding method.

Type #1 - twisted pair
To make it possible, after reading the designation, to obtain the necessary information about twisted pair, an international classification of cables was invented.
The classification is based on the formula: AA/BCC. Here the first pair of characters is "AA" indicates the presence of a shared screen.
Symbol "IN» informs about the availability of individual protection for each pair. The last two characters will tell you about the type of twist. If this "TR", then the conductors are twisted in pairs. When "T.Q."- there is a twist in fours.

The presence of protection is a special characteristic of twisted pair.
A lot of information can be found by reading the label:
- Unprotected couple. This is a cable without a protective shield. The conductors are placed in ordinary plastic. Such a pair is marked with the abbreviation U/UTP.
- Foil pair. The cable has one shield for all pairs. Marking - F/UTP.
- Unprotected couples. A single screen consisting of a braid. Mark the cable with a combination of symbols S/UTP.
- Foil protection for couples. Plus, there is a common copper screen. Marking - S/FTP.
- A foil screen protects the vapors. There is no shared screen. Designation - U/FTP.
- Overall screen made of foil plus braid. Couples without a screen. Marking - SF/UTP.
- Foil shield for both couples and general protection. Designation F/FTP.
- Foil screen for couples. As a general screen - foil and braid. Recognized by markings SF/FTP.
This list shows the designation according to the international classification of twisted pair cables. Our generally accepted designations are slightly different.
This type of Internet wire, such as twisted pair, can unite devices located no more than 100 m from each other into one network.
If you plan to use this type of cable, we recommend checking out the best connection methods twisted pair wires between each other.
Type #2 - fiber optic network cable
Today, there is no faster technology for transmitting information on the Internet than optical fiber.

Through fiber optic cables stretched along the ocean floor, high-speed Internet connects not only cities, but also continents.
The advantages of optical cable include:
- good throughput data;
- durability;
- speed of detection of unauthorized access, which increases network security;
- noise suppression, sufficient degree of protection against interference;
- significant speed of information transfer;
- possibility of implementing additional options.
Fiber optic cables come in single-mode and multimode types. They differ from each other in the modes of propagation of light rays in the cable.
Despite the low cost and all the other advantages of this type of cable, there are two factors limiting their use - equipment and adapters for a fiber-optic network are very expensive.
Cable termination is performed using expensive equipment. Installation and repair of the network is not easy; only highly qualified specialists can perform the work. For this reason, fiber optic cable is used in large networks.
Type #3 - coaxial wire
The main characteristic is wave resistance. The quality of the cable and the transmitted signal depends on it.These values are affected by the material and its dielectric constant, as well as inductance, capacitance, and resistivity. The signal strength depends on the transmission distance.
There are two types of cables of this type: thin and thick. The diameter of the first is no more than 0.5 cm. Its specific features are increased flexibility and rapid signal attenuation, so the signal is transmitted over short distances at speeds of up to 10 Mbit/s.
Thin cable belongs to the category RG-58/U. Its characteristic impedance is 50 Ohms.

The cross-section of a thick coaxial cable is 1 cm. Since its rigidity is increased, installation is carried out using expensive special devices.
The thick cable itself is also twice as expensive as the thin one. It belongs to the category RG-11 or RG-8. In the first of the models the resistance is 75 Ohms, in the second - 50 Ohms.
The ability of a conductor to accumulate charge is characterized by inductance and linear capacitance. Brief characteristics are contained in the labeling.
So, in the notation KMG the first letter stands for TO - coaxial, second - M - mainline, G - laid in the sewer. KMK — there is armor for underwater installation.
There was a time when this type of cable was found in many areas. Some of its characteristics are even higher than those of twisted pair cables. Nowadays, coaxial cable is still used for laying routes for analogue cables. CCTV systems, while twisted pair is used to connect IP video surveillance systems.
However, over time, the latter began to supplant coaxial cable. Users appreciated its simpler and faster installation, as well as its lower cost.
Network cable device
The design of each type of cable is different. The simplest design is for a coaxial conductor, the most advanced is for a fiber optic conductor.
Structure of a coaxial cable
Even at the dawn of the creation of networks, only coaxial cable was used. Its structure includes a central conductor.
Around it is a thick layer of insulation, followed by braiding - aluminum or copper, and finally - an insulating shell.

Twisted pair device
The most common wire for the Internet is twisted pair. This cable allows you to connect all computers, as well as other necessary devices, through one channel. Makes it possible to ensure that certain users can use information from all computers.
Most often, they buy the required piece of this wire, crimped on all sides with connectors. Less often they take a simple piece of twisted pair, but crimping performed after installation, using the correct pinout diagram.
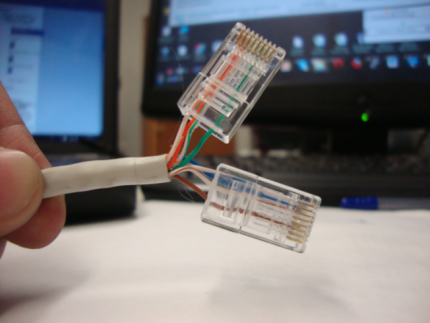
The shielding layer can be located in only two places - on top of a separate pair, and then it is called individual, and on top of all pairs, then it is called common.
Features of the optical cable structure
This modern cable has a special design structure. It is formed by the finest wires, and a special coating separates them from each other.
These wires are conductors of optical rays that carry information as they pass through the silicon cores found in each fiber. In addition to the core, the fiber has an optical cladding, protection, and a buffer coating.
The components of a fiber optic cable are elements such as the central core and the sheath that surrounds it.

Like the core, the “shirt” consists of glass, but the parameter such as light refraction is less. Light rays, reflected from the glass, diverge along the core, but do not go beyond it.
Cable selection criteria
This cable has many characteristics, but only some of them are important for selection. These include: conductor category, core type, shielding method. Let's look at each of them in detail.
Criterion #1 - Internet cable category
There are seven categories of twisted pair cable—from Cat.1 to Cat.7.
Cords of different categories differ in the efficiency of the transmitted signal:
- First category Cat.1 has a bandwidth of only 0.1 MHz. Such a conductor is used to transmit voice data using a modem.
- U category Cat.2 bandwidth - 1 MHz. The data transfer speed here is limited to 4 Mbit/s, so this conductor is considered obsolete and is almost never used.
- For category Cat.3 frequency band - 16 MHz. Data transfer speed - up to 100 Mbit/s. Used to create local and telephone networks.
- Cat. 4 - cable with a maximum bandwidth of 20 MHz. Data transfer speed - no more than 16 Mbit/s.
- Cat.5 has a maximum bandwidth of 100 MHz and a maximum data transfer rate of 100 Mbit/s. Areas of application: creating telephone lines and local networks.
- Cat.5e has a bandwidth of 125 MHz. Speed - up to 100 Mbit/s and 1000 Mbit/s (for four-pair wire). This cable is the most popular when building computer networks.
- For Cat.6 acceptable frequency band is 250 MHz. Transfer speed is 1 Gbit/s over a distance of up to 50 m.
- U Cat.6a transmission tape - 500 MHz. Speed – up to 10 Gbit/s within a range of up to 100 m.
- Cat.7 has a bandwidth of 600-700 MHz. The speed of this wire for the Internet is up to 10 Gbit/s.
- Cat.7a. Bandwidth - up to 1200 MHz. Speed – 40 Gbit/s for a length of 15 m.
The higher the cable category, the more pairs of conductors it contains. Moreover, in each pair there are more pairs of turns per unit length.

Criterion #2 - type of cable core
The cable cores are divided into copper and copper-plated. The first type is considered to be of higher quality.

They use a cable with such a core for an extensive and fast network - more than 50 m. The second type is somewhat cheaper, and the losses in it are not so great.
Its core is an inexpensive cable with low conductivity. It is coated with copper, which has high conductivity.Since current flows through the copper side of the conductor, conductivity suffers only slightly.
When purchasing a copper-plated cable, you have to make a choice between two types - CCS And CCA. The difference between them is at the core. For CCS it is a steel conductor, for CCA it is made of aluminum. The second one is not much different from the copper one.
Installing a steel conductor can be difficult, since steel, as a not very elastic material, is susceptible to breakage.
Over a limited distance, the discrepancy between copper and copper-plated cable is not noticeable. If the distance is more than 100 m, a cable with an aluminum core simply will not transmit the signal.
The reason for poor commutation is that aluminum has a higher resistance than copper. As a result, the output current has insufficient power and the network components do not “see” each other.
Criterion #3 - cable shield
The shield is necessary to protect the conductor from electromagnetic noise from other cables. It must also compensate for the radiation of the electromagnetic field of the twisted pairs themselves.
If there are nearby power cables up to 380 V with a core cross-section of less than 4 square meters, one screen is required. In this case, the best option would be a cable FTP.

When it is expected to be adjacent to a conductor from 380 V with a core cross-section of up to 8 squares, a double screen will be required. A good option - F2TP.
The proximity of high-voltage cables from 1000 V with a core of 8 square meters requires the laying of both power and network cables in individual corrugations. Screen option - SF/UTP.
Such cables are not used in everyday life.The most commonly used cable here is unshielded cable belonging to the category 5e type UTP.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
About choosing a cable for the Internet:
Video about the features of network cable marking:
When using an Internet cable, you should follow the instructions for its installation. The presence of a large number of different conductors allows you to choose a model for specific conditions.
Having studied the properties of all types and knowing how to decipher the markings, you can make the most correct choice.
Would you like to supplement the above material with comments and useful tips for choosing? Or noticed inaccuracies/inconsistencies in information? Write your opinion and recommendations under our article.
Or maybe you are just selecting a suitable cable and want to clarify a number of nuances? Ask your questions to our experts and other site visitors in the comments section.




All the time I wanted to pick up such information, but somehow I never got around to it. All damaged Internet cables were simply replaced with new ones. Now it’s probably easier to get rid of this tangle of wires altogether and make all communications wireless. The prospect of living under the influence of various types of radiation is a little frightening, but at least they (the radiation) are not visually annoying.
It is necessary to run a cable from the router to the SmartTV set-top box. What kind of wire is needed for this? The length needed is approximately 2.5 meters.