Thermocouple for a geyser: design and principle of operation + testing and replacement on your own
The designs of modern gas water heaters and boilers are equipped with a number of different sensors. This is an obvious point, given the fully automatic operation of such equipment.Using sensors, various system operating parameters are analyzed, and the end result is the correct adjustment of gas equipment to the appropriate operating mode.
One of the important technological sensors is a thermocouple for a gas water heater, which monitors changes in operating temperature. In this article we will talk about the design and principle of operation of a thermocouple, and methods for checking its functionality. We will also consider how you can replace this element with your own hands.
The content of the article:
Design and purpose of a thermocouple
Sensor elements, which are structurally a thermocouple, have found wide application not only in household appliances, but also in industrial equipment. Essentially, a thermocouple should be considered a thermoelectric converter.
Typically, such a converter is used to measure ambient temperature. In particular, if you examine how a thermocouple works in the design of a gas boiler, you can note that thanks to such a sensor, the temperature of the gas burner flame is monitored (measured).

Design features of the thermocouple
The design of the thermocouple is not particularly complicated, but from a technological point of view, the manufacture of this element requires high precision and compliance with the characteristics of the components used.
Actually, the main components of the sensor are two metal elements with different physical properties.
These elements (wires) are soldered at the ends on one side, while the end parts of the other side remain free - they are used to connect to the thermo-EMF converter and transmit the potential difference.
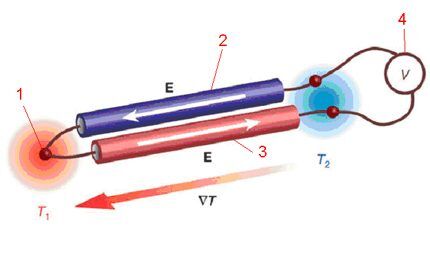
Operating principle and purpose of the sensor
The thermoelectric effect (in other words, the Sebbeck effect) determines the operating principle of the device in question. Conductors made of different metals connected at one point form a potential difference, taking into account the fact that different metals have different thermo-EMF coefficients.
In relation to a gas water heater, the operation of a thermocouple provides combustion control and protection from possible gas contamination. When the burner of a gas boiler or water heater operates in active mode (throws out a flame), a thermocouple installed in the flame zone generates an electric current under heating. The current is sufficient to control the opening and holding of the gas valve.
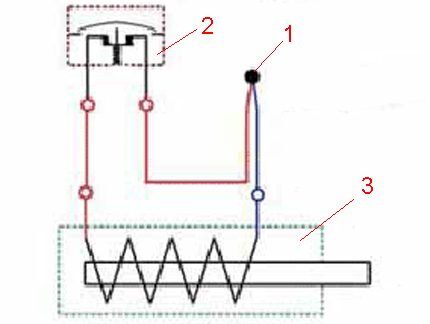
If the heating temperature drops sharply (burner flame goes out), the amount of current generated also decreases, which results in the closing of the gas valve. Accordingly, the gas supply to the system is blocked, which ensures safe operation of the equipment.
If the gas valve on your gas water heater does not work, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with inspection and repair methods.
Checking the thermocouple of a home geyser
Long-term operation of a home geyser fully allows for such a moment when the thermocouple fails. In this case, it is necessary to check the functioning of the system and, accordingly, check the control sensor itself.
Of course, not all owners of gas equipment are able to perform such work. And from a security point of view, the best solution would be to contact gas company to solve such a problem.
But at the same time, situations may be different, including the impossibility of contacting specialists for some reason. Then the only option left is to try to do the work yourself.

In this scenario, a user inexperienced in gas matters is interested in how to check the thermocouple on a gas boiler using a tester - a common electrical and electronics diagnostic device. Let's try to reveal this technological point in order to make the task easier.
Stage #1 - preparation for testing by a tester
To begin with, let us remind you that a tester is a measuring device - pointer or digital, with which it is possible to measure:
- resistance;
- voltage value (AC and DC);
- current strength (AC, DC).
The measured values marked are sort of basic. Moreover, modern testers are able to check a number of other parameters, for example, inductance or capacitance.
But taking into account the principle of operation of the thermocouple of a household gas boiler, the voltage measurement mode in the millivolt range is quite sufficient.

In addition to the measuring instrument (tester), the installer will need another fairly simple tool - a heating source. It is better if such a source has the ability to emit an open flame. Therefore, the best option here would be to use a regular paraffin candle.
Stage #2 - visual inspection for defects
The procedure for testing the flame control sensor is simple. However, before proceeding with the hot test, it is recommended to carefully examine the thermocouple visually from the outside.
When inspecting the area of the junction and the descending rod, physical defects of the metal, including burnout areas, should not be visible on the surface.
Stage #3 - testing the sensor's performance
After completing the visual inspection, you can proceed directly to the hot test. To do this, the junction area and the downward section of the gas column thermocouple rod are placed above the candle wick.
Next, a measuring device (tester) is connected to the terminal ends of the thermocouple, after which the candle is lit. The generated potential is observed on the working scale of the measuring device.

The absence of any electrical potential readings clearly indicates a sensor malfunction. In case of partial defects, chaotic (unstable) readings of units of millivolts may be observed on the measuring device. If the geyser sensor is working properly, a stable value equal to tens of millivolts (20-30 mV) is usually recorded on the device.
Moreover, as the thermocouple body is heated by a candle flame, the readings on the instrument scale change slightly upward. If the candle flame is extinguished, the tester readings will tend to zero as the rod body and junction area cools. That's all. With this development of events, the thermocouple, as being in good working order, can be safely placed at the site of action.
How to replace a temperature sensor?
Most options for repairing (replacing) the thermocouple of a household geyser require dismantling this element from the equipment structure. Accordingly, a potential technician needs to be aware of how to remove and install the sensor. Let's look at how to replace a thermocouple in a gas boiler and what is needed for this.
The tool set is quite simple. Usually one or two open-end wrenches are required for a 14 (or 15) nut.
It is worth noting that, based on the specific boiler model, the size of the fastening nuts may differ, as well as the design of the thermocouple itself. On some models, the thermocouple is secured with screws.

Thus, the technician needs to free the sensor from the mounting screws, after which the structure is removed and can be repaired or replaced with a new one. Installation of the new element is carried out in the reverse order.
Are you having problems with your geyser thermocouple? In this case, we recommend that you read repair and replacement manual.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video below demonstrates the process of testing a thermocouple installed on one of the models of gas boilers.
The video explains in detail how to remove, check, change an important component of a gas water heater, without which the equipment actually remains operational only in uncontrolled mode, which is extremely dangerous for the end user:
Replacing the sensor yourself is possible.However, for this, the home craftsman must have plumbing skills and be able to use measuring instruments:
Thanks to the thermocouple, the ignition and heating process is automated, increasing the safety of the gas water heater and boiler. The material considered allows us not only to fully appreciate the technological significance of the thermocouple device in the design of gas-using equipment and to understand the structural intricacies of home boilers, but also, if necessary, to repair the equipment with your own hands. At the same time, it is important to remember the safety rules, and if you have doubts about your own abilities, it is better to turn to specialists.
Would you like to talk about your personal experience of testing the functionality of a thermocouple? Or do you have useful information on the topic of the article and would like to share your knowledge with other users? Write your comments, participate in discussions - the feedback form is located below.



