The best way to insulate an attic: the best thermal insulation materials for arranging an attic roof
An attic is a comfortable attic, which is often used as a living room or additional technical space. It differs in that it requires enhanced thermal insulation, since it has a large contact area with the cold atmospheric environment.
Depending on the purpose of using the attic, insulation materials are chosen that differ in the degree of thermal conductivity, density, and flammability. Let's figure out how best to insulate the attic so that it turns from a cold attic into a room suitable for living or storing things.
The content of the article:
Warm attic - additional living space
No matter how large the room is, there is always a need for one more room - a guest bedroom, a playroom, a gym, or just a convenient storage room.
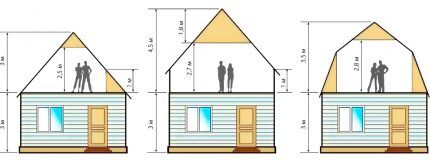
According to regulatory documentation, an attic is a room formed by a facade and roofing. According to sanitary standards, the distance from the floor to the line of intersection of the wall with the roof should be at least 1.5 m, and to the ceiling - 2.5 m. In this case, an area with a “high” ceiling (2.5 m or more) should occupy from 50 % of the total attic area.
It is obvious that in private housing construction there are deviations from the standards.For example, the configuration of the attic space can be influenced by factors such as the shape and size of the roof: houses with a high roof have higher attic ceilings, but the floor area is narrower.

To increase the size of the attic, they resort to various techniques: increasing the height of the lower tier of the sloping roof, making the facade walls higher. Interesting attic design options can be viewed on the Roofing Guide website.
However, with all the advantages of an additional comfortable room, there are nuances that increase the cost of construction and finishing work:
- window installation;
- ventilation equipment;
- hydro- and thermal insulation.
The last point is also important because literally everything will have to be insulated: the floor, gables, walls, often consisting of two parts - the facade and the roof. At the same time, the same requirements apply to thermal insulation materials as to insulation for residential premises. In addition to suitable technical characteristics, they must be absolutely safe.
Review of thermal insulation materials for roofing
Today on the market you can find everything: from long-proven glass wool to natural and foil materials, which are still less commonly used in practice. Let's consider the best way to insulate the walls and floor of the attic from the inside so that the attic space becomes warm and does not have to be repaired in the near future.
Option #1 – glass wool
Glass wool has gained popularity due to its low cost, so if you want to save on thermal insulation, you can use rolled mats or slabs that are more convenient for installation. The raw materials for production are specially purified quartz sand and glass industry waste.

In addition to affordable cost and light weight, the material has the following advantages:
- elasticity, which allows you to lay slabs or mats with a tight fit to each other and to the rafters;
- flexibility, useful for insulating complex roof areas;
- unattractiveness to rodents, which is explained by the lack of natural materials in the composition.
However, there are also plenty of shortcomings. For example, these include high hygroscopicity, which requires the use of vapor barrier on the inside and ventilation to evaporate moisture on the outside.
Due to its fragility, fiberglass breaks down and tiny particles of dust spread into the air, creating a hazardous environment for health. In addition, dubious companies use formaldehyde as a binder in production, so it is better to use a more expensive but safe material.

For example, the “Pitched Roof” from the “Isover Geo” line is not only safe for residents, but is also a non-combustible material.
Option #2 – mineral wool
Unlike glass wool, mineral wool is made from the melt of igneous rocks, which, when processed, form a less brittle, more durable and elastic material. Accordingly, the performance properties of this insulation are higher.

Hygroscopicity is lower than that of glass wool, but moisture absorption still occurs, so it is not worth abandoning the vapor barrier during installation work. Vapor permeability is within normal limits, and if proper conditions are created for the evaporation of moisture from the surface, the material will last a long time.
Branded products do not contain harmful substances, which is guaranteed by a sanitary certificate. If you doubt the safety of thermal insulation, ask to see documentation when purchasing.

Modern basalt insulation is easy to install, which is accompanied by some developments by manufacturers. For example, ROCKWOOL boards have a spring-loaded edge zone that provides a tight fit, security and stability.
The main disadvantage of the popular brands popular among builders - TechnoNIKOL, PAROC, Izovol, ROCKWOOL - is considered to be cost.
Option #3 – ecowool
A real discovery was a material produced on an organic basis - ecowool.Cellulose fibers, which are obtained by processing wood, cardboard, and recycled materials, demonstrate excellent thermal insulation qualities.

In many technical characteristics, ecowool “steps on the heels” of mineral analogues:
- thermal conductivity – 0.038-0.043 W/m×°C;
- degree of flammability – G2 (self-extinguishing, low-flammability);
- layer density – 45-75 kg/m³.
The name “ecowool” speaks for itself - the material is considered environmentally friendly and does not contain hazardous toxic substances. However, thanks to the treatment with antiseptics, it does not attract rats and is protected from rotting.
The downside of ecowool is its high degree of hygroscopicity, so the installation estimate, in addition to rolled or sprayed material, should include hydro- and vapor barrier polyethylene films or polymer membranes.
There are two methods of laying ecowool when insulating an attic: “dry” and “wet”.

For the “wet” method of applying ecowool to roof elements from the inside, an adhesive solution is used, which ensures maximum adhesion of the material to the base and increases the strength of the heat-insulating layer.
The main disadvantage of insulation is the presence of special equipment for installation.Installers must have special skills; without initial experience, it is better to choose materials that are easier to install - for example, mineral wool in slabs.
Option #4 – polystyrene foam
Inexpensive, but dubious material for insulating attic spaces. Let's try to figure out why foam plastic, which is still popular, is undesirable and even dangerous to use in the process of thermal insulation work.

However, the shortcomings of the material become powerful arguments against its use.
The disadvantages include the following:
- often foam plastic does not meet the declared characteristics, since it is produced everywhere without taking into account any technical requirements;
- it is a flammable material that releases toxic substances during a fire - as is known, people die in the first minutes after a fire not from fire, but precisely from poisoning by combustion products;
- polystyrene foam quickly collapses - it breaks up into individual granules, as a result of which its thermal insulation qualities are lost.
Manufacturers who take the quality of their products seriously take measures to improve them. However, even slabs from well-known brands are inferior in characteristics to other materials. By the way, in European countries, foam plastic is prohibited for use in the residential sector, while our compatriots continue to save money and put their families at risk.
Option #5 – extruded polystyrene foam
Another thing is slabs made of extruded polystyrene foam, which differs in both production technology and performance characteristics.

EP is more expensive than polystyrene foam, but the advantages of the material make you turn a blind eye to the difference in price and prefer it.
The advantages of extruded polystyrene foam include:
- thermal conductivity coefficient - on average 0.030 ±0.032 W/m×°C;
- very low degree of hygroscopicity;
- consistent slab geometry that does not change over time;
- strength due to protection from water ingress;
- flammability class - G2, characterized by self-extinguishing.
Unfortunately, during a fire, polystyrene foam also releases toxic substances, although not to the same extent as polystyrene foam - you should not forget about this.
Thanks to complex production technology, there are almost no counterfeits on the market - only serious enterprises can afford to produce insulation.
The disadvantages include rigidity and lack of elasticity. Unlike elastic mineral wool, EP slabs are difficult to adjust to certain sizes so that after installation there are no gaps between them. Typically, the gaps between them are filled with foam or other sealant.

This method is often used when they want to create a loft-style interior: beams exposed openly under a layer of insulation and inner lining look more than picturesque.
There are leaders among manufacturers of extruded polystyrene foam. For example, the products of the Penoplex brand are widely known, the name of which has already become a household name. High-quality slabs are distinguished by the fact that they do not require the mandatory use of waterproofing and are quite suitable for creating a continuous roof sheathing.
Rules for working with extruded polystyrene foam are described in this material.
Option #6 – sprayed polyurethane foam
Spraying foam thermal insulation on the inside of the roof is an excellent opportunity to create seamless, durable insulation without cold bridges and seams that require filling. One of the highest quality “sprayers” is polyurethane foam, which creates an effective thermal insulation layer.
Advantages of sprayed insulation:
- thermal conductivity coefficient – 0.03 W/m×°C and less;
- optional use of vapor barrier;
- good adhesion to various surfaces;
- lack of preliminary preparation;
- minimal load on rafter structures.
The thin but dense layer created by hardened polyurethane foam is also excellent soundproofing protection, which is important for an attic used as a bedroom.

Insulating polymer foams, among other advantages, have an anti-corrosion effect: metal parts treated with polyurethane foam do not rust, receiving additional protection. Polyurethane foam also does not allow moisture to pass through, therefore it is considered an excellent waterproofing material.
The disadvantages include high cost and the need for spraying equipment. It is not possible to carry out thermal insulation on your own without special education, so another cost item is the services of a team of trained installers.
Option #7 – PIR boards
Not long ago, a material appeared on the market that combines the positive qualities of popular insulation materials: the thermal conductivity of polyurethane foam, the strength and hydrophobicity of extruded polystyrene foam, and the fire resistance of mineral wool. These are PIR boards - products made from polyisocyanurate foam, which has a rigid structure with small cells filled with gas.
The main achievement of PIR board manufacturers is considered to be a thermal conductivity coefficient reaching 0.022 W/m×°C.

In addition to conventional plates, foil-coated products are also produced, additionally protected from moisture by a thin metallized layer. The slabs are connected to each other by tongue-and-groove locks, which makes it possible to create voluminous seamless areas on flat surfaces.
Leaders among enterprises producing insulation materials have already adopted new developments and are producing PIR boards under their own brands.For example, products from the Technonikol company are becoming popular, and the manufacturer specializes in the production of insulation for all types of building structures.

The wide distribution of products with superior technical characteristics is hampered only by high cost. 13-15 thousand rubles. per cubic meter of material is really expensive compared to mineral wool or expanded polystyrene.
In addition to the listed best types of thermal insulation for the attic, mats made of natural wool, expanded clay and even fibreboards are also used, however, these materials are not so common due to unsuitable characteristics for some reason or have complicated installation technology.
Methods for insulating floors in the attic
No matter how warm the walls in the attic are, the floor must also be insulated, especially if the room will be used as a bedroom or playroom. We must not forget that this is also insulation of the ceiling of a one-story house or the top floor of a 2-3-story building.
When insulating an attic floor, you must remember two conditions:
- the material should be light and not create a load on the floor;
- thermal insulation characteristics must be at a high level.
Taking these requirements into account, you can use glass wool, ecowool, mineral wool, extruded polystyrene foam, and PIR boards. The insulation is laid under the finishing sheathing, for which treated boards are usually chosen.
Advantages of insulation:
It is difficult to give exact advice on what material is best to decorate and insulate an attic, since much depends on the climate in the region, the size of the attic space, the characteristics of the roofing and the rafter structure itself. Not least important are the financial capabilities of the homeowner.
We also recommend reading step-by-step instructions on how to insulate an attic yourself. More details - go to link.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
An example of insulating an attic with mineral wool:
Thermal wool blowing technology:
A universal material is stone wool. Full review from the manufacturer TechnoNIKOL:
When choosing insulation, do not forget that the attic is a living space that should not only be warm, but also safe. If possible, purchase materials that meet sanitary standards, have a suitable flammability class and are free of toxins.
And the best characteristics of thermal conductivity, stability and hygroscopicity are a guarantee of comfortable use of the room for a long time.
Which attic insulation material did you prefer and why? Are you satisfied with the result? Please share your opinion with our site visitors. Leave your comments in the block below.




Polystyrene foam and all its more fashionable and modern derivatives are easy to install, but are too fire hazardous. This stops me. I know that there are self-extinguishing ones, but they are too expensive. So for now I'm leaning towards basalt.