Insulation for heating pipes: overview of types + application examples
Owners of private houses often consider thermal insulation of heating system pipelines to be an unnecessary waste of money.But such measures are a direct path to significant savings in thermal energy.
The reduced amounts in bills from energy companies and for fuel for the boiler will certainly cover the costs of thermal insulation. You just need to choose the right insulation for heating pipes so that it lasts longer without losing its characteristics, and we will tell you how to do it.
The content of the article:
Why do you need to insulate heating pipes?
Typically, cottage owners insulate only those heating pipelines that are located outside the home. There, heat losses are most likely and large-scale. It’s not for nothing that all city heating mains are so thoroughly insulated. You also need to choose very carefully heating pipes.
Energy workers have already learned to count their money. However, the pipes of the heating system in the basement or boiler room should also be insulated. Heating such non-residential premises in a house is a waste of money.

There are five good reasons to cover heating pipes with a heat insulator:
- Protection of coolant from freezing.
- Prevents condensation.
- Reduced heat loss.
- Extending the “life” of boiler equipment and pipelines.
- Possibility of laying external sections of the heating system in the ground above its freezing point.
Pipes are insulated in the basement, attic, boiler room and outdoor areas. It is not worth installing insulation on risers inside the house in living rooms. If you do this, the heat will still enter the room, but after radiator. There is no point in such actions. Money will be spent on a heat insulator, but it will be of no use.
When the coolant moves through insulated pipelines, it does not waste thermal energy. All the heat goes to heating the necessary rooms. At the same time, the boiler and pumping equipment in the boiler room do not have to operate at maximum settings in order to maintain a comfortable temperature in the rooms.

Another couple of disadvantages of heating pipes without insulation are condensation and freezing. In operating mode, when the system circulates coolant, most often - heated water; there are no problems with its freezing inside and condensation outside. But during accidents on the heating network, the pipelines begin to “get wet” and then freeze.
Thermal insulation material in such a situation provides several additional hours, during which the coolant cools down, but not so quickly.
In general, insulation of heat supply pipes is carried out:
- when laying heating system communications outdoors;
- on sections of pipelines located in unheated basements and attics;
- when installing heating mains and branches from them onto risers in the basements of apartment buildings.
Insulated pipes provide warm batteries while reducing energy costs.Here it is better to spend money on thermal insulation materials rather than pay huge heating bills. It is always more effective to insulate than to spend money on fuel for a stove or boiler.
Review of insulation materials on the modern market
All thermal insulation materials for heating pipes are divided into:
- roll;
- cylindrical with and without a cut;
- semi-cylindrical (“shells”).
The first ones are sold in rolls; pipes are wrapped with them. The latter are a cylinder made of insulation with an empty core into which a pipe product is inserted. The third ones are two halves in the form of semi-cylinders, which are applied to the pipeline from below and above, resulting in thermal insulation protection on all sides.
The good thing about the roll version is that it can be mounted on pipes of any diameter. Cylindrical materials are installed on pipelines of a specific size only. If they are installed on a product with a larger cross-section than they are designed for, a gap will form in the heat-insulating layer. The effectiveness of insulation in this case will sharply decrease.
Depending on the type of insulation, “cylinders” and “shells” are soft or hard. In the first case, the insulator can be bent for installation at a bend in the pipeline, and in the second, similar sections of the heating system are left without an insulating coating.
Type #1 - fiber wool
Glass wool and basalt mineral wool in rolls are classics of insulation. These materials are cheap, easy to install and have decent thermal insulation characteristics. Their main disadvantage is their high hygroscopicity. They absorb moisture well, immediately losing all their insulating properties.

Stone (basalt) mineral wool is least prone to absorbing moisture. Glass wool is a little inferior to it in this regard. There is also a slag option, but it is better to abandon it immediately. This type of mineral wool has the highest hygroscopicity. For insulation of heating pipelines, water supply and the sewer cannot be used.
Installation of mineral wool on pipes is carried out with an overlap, followed by fastening the insulation on top with steel tape or stainless steel wire. In terms of thermal conductivity, both mineral wool options recommended for heating systems are similar. This indicator varies between 0.035–0.044 W/(m*0WITH).
When using mineral wool, you must remember that over time it shrinks and thickens. As a result, the effectiveness of its thermal insulation decreases. It’s worth laying down a thicker layer right away so that in a couple of years you don’t return to your original position and have to start laying insulation on the pipes all over again.
Glass and basalt mineral wool will last about 10 years. But this is only on condition that it will not get wet and be subject to mechanical stress.
Type #2 - foamed polymers
This category of pipe insulation includes materials based on:
- polyethylene;
- expanded polystyrene (foam);
- polyurethane foam;
- rubber.
The first of these heat insulators is offered in stores in the form of a roll of material made of several polyethylene layers with air bubbles between them, as well as in the form of sleeves made of foamed porous polyethylene.
The thermal conductivity of this insulation is around 0.035 W/(m*0WITH).It is not afraid of moisture and remains elastic even in severe frosts.

Expanded polystyrene heat insulator for heating pipelines is produced in the form of two half-cylinder shells. To ensure the absence of gaps and cold bridges, many manufacturers make them with tongue-and-groove locks along the length. For large-diameter pipes there may be not two, but three or four segments. Thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam is 0.037–0.042 W/(m*0WITH).
Polyurethane foam is similar in density and other characteristics to its polystyrene foam counterpart. Only it is slightly superior to the latter in terms of thermal insulation quality. The thermal conductivity of this insulation is 0.035 W/(m*0WITH).
It is most often used for insulating large pipes in factories. Such finished products are used when laying heating mains inside neighborhoods and for installing outlets from general networks to cottages.
Polyurethane foam insulation for intra-house pipelines is produced in the form of hard shells with an outer layer of sheet steel. This polymer is afraid of ultraviolet radiation and needs protection from light.
Foam rubber has the same characteristics as its polyethylene counterpart in most respects. However, it has a larger operating temperature range (from -190 to +175 °C) and is much more expensive. It is most often used for thermal insulation of ventilation systems and pipes with refrigerant, where its properties are more in demand.
Type #3 - combined materials
Mineral wool is prone to moisture accumulation and loss of thermal insulation properties. Polymer insulation is fragile and resistant to fire; ideally, they need additional external protection.To obtain heat insulators with the necessary characteristics, many manufacturers combine them with each other and with other materials.
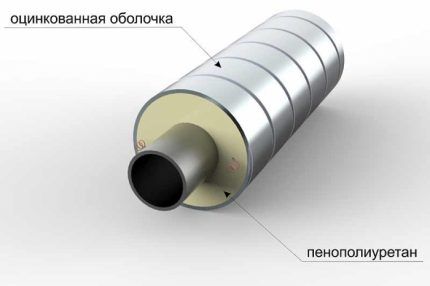
Combined pipe insulation materials include:
- polyethylene with an outer foil layer;
- polymer shells with a steel shell on top;
- mineral wool with waterproofing protection made of polyethylene or foil.
Also in stores you can find thermal insulation materials with a self-adhesive layer. They are easier to install and attach to pipes. The joints of such insulation are sealed without cold bridges. However, its price is slightly higher than its conventional counterpart.
It is not recommended to use aluminum foil alone without an insulating layer of polymers or mineral wool for thermal insulation of heating pipes. Its thermal conductivity is too high. It can only be used as an additional layer.
Type #4 - paints and spray foams
In addition to ready-made factory-made insulation materials, which only need to be placed on the heating pipe and secured to it, there are various painting and spraying compounds. The latter are superior to “shells” and rolled analogues in terms of the quality of connection to the surface of the pipeline and the tightness of the thermal insulation layer.

Sprayed polyurethane foam is an excellent insulation material that covers the pipeline with a monolithic layer on all sides. However, you can’t even think about its temporary dismantling to repair the heating pipeline.It’s difficult to call this task easy.
Plus, polyurethane foam breaks down over time when exposed to ultraviolet rays. It is best to use it only in basements that are closed without windows, and when installed outdoors, be sure to cover it with other building materials to protect it from the sun.

Thermal insulating paint consists of:
- ceramic microspheres;
- perlite;
- acrylic resins.
Using this paint you can cover all the bends of the heating pipe. It has excellent heat-protective characteristics. But experts recommend using it only as additional insulation in addition to the main classic one.
In addition to all of the above materials, you can use simple expanded clay for pipe insulation. He is not afraid of fire and moisture. Plus it's very cheap. To provide thermal insulation around the heating main, it is necessary to make a box of boards or metal.
And then pour expanded clay inside the latter so that the pipeline is covered with sprinkling on all sides.
Which insulation option is better?
When choosing insulation for heating system pipes, you must consider:
- Location of the line (in the ground, in the basement, in the attic).
- Presence of problems with rodents.
- Financial opportunities.
- Pipe diameter and pipeline configuration.
- Coolant heating temperature.
In practice, rats and mice only avoid glass wool. Plus the paint is simply too much for them. They may well chew through the rest of the insulation in order to fill their nest.

Polyethylene in all its variations is resistant to the aggressive effects of cement. If a pipe with insulation is laid in a wall and then the hole is filled with concrete, then polyethylene material should be preferred.
Polyurethane foam allows you to reach all sections of the highway, reliably covering it with a monolithic thermal insulation layer. However, special equipment is required to apply it. Plus, it is difficult to spray such insulation onto thin pipes; most of the foam will end up on the surrounding walls.
When installing a heating system in areas with unstable soils and connecting several buildings to one boiler, the most optimal insulation is lightweight polyethylene or thin polystyrene foam. It is not worth using heavy stone wool here. When the soil moves, highways may not withstand additional loads and burst.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
When choosing insulation for heating system pipelines, it is necessary to take into account several factors. To make it easier for you to understand this issue, we have made a selection of video materials. The above reviews and comparisons will certainly help you navigate the selection of heat insulators for pipes.
Insulation of the street pipeline from the boiler room to the house:
Review and installation rules for Energoflex insulation tube:
Technology of pipe insulation with foamed foam insulation:
It is not difficult to insulate heating pipelines; you just need to choose the right insulating material.For heating mains in the ground, it is better to prefer moisture-resistant and rigid insulation with an outer shell of steel, and for areas in the attic it is worth taking lightweight mineral wool.
All of them allow you to reduce the cost of heating your home and increase the efficiency of the entire heating system. It is only necessary to choose their thickness correctly, guided by SP 41-103-2000.
If you have any questions or want to supplement the material with valuable information on the topic, please leave comments under our article.




The pipes in our house run three meters underground, so even the most severe frosts are not terrible, but in the bathhouse they already go from above, so they were insulated right away at the initial stage of construction. We immediately chose glass wool for insulation; the price is reasonable and various rodents will not be able to damage it. It's been two winters without any problems, the main thing is to additionally protect it from moisture outside.
You write too categorically that rodents are not interested in glass wool. Yes, they gnaw on it less willingly, but when there is no choice, they can build a nest in it.