How to calculate the power of an air conditioner and choose the right unit for your needs
Correct calculation of air conditioner power is the key to efficient, uninterrupted operation and durability of climate control equipment.The choice of performance is based on the overall dimensions of the room and related factors contributing to the accumulation of thermal radiation.
Taking into account all the parameters and nuances of operation allows you to provide an optimal power reserve, but at the same time not overpay for the super-performance of the split system.
But how to correctly perform the necessary calculations? We will consider this issue in detail in our article. In addition to the two methods for calculating power, we will focus on other important criteria that influence the choice of air conditioner.
The content of the article:
- What do the power values in the documentation say?
- BTU value and labeling explanation
- Electricity consumption and energy efficiency assessment
- Methods for self-calculation of power
- Step-by-step calculations of equipment power
- Additional criteria for choosing an air conditioner
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
What do the power values in the documentation say?
The technical documentation for air conditioners indicates two or three types of power. The indicators characterize different operating parameters: cooling and heating capacity, as well as the electrical power consumed by the split system.
The range of indicators can be misleading. In heating electrical appliances, such as a boiler or radiator, the heat output corresponds to the energy consumed. For an air conditioner, these parameters are different.
A split complex, unlike a heater, does not directly convert electricity, but uses it to operate a heat pump. The latter is capable of pumping much more heat energy than the electrical power consumed.
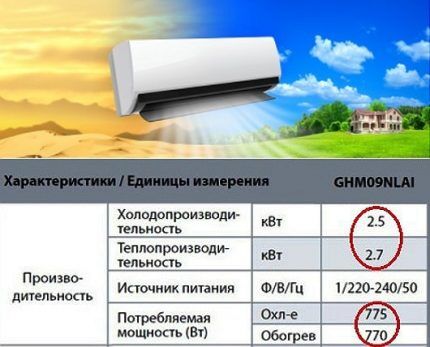

Cooling power is indicated in kW, the range of values for household equipment is 2-8 kW. In addition, many manufacturers use the British marking - BTU (BTU) in technical descriptions.
The cooling capacity of the split unit must correspond to the service conditions. Otherwise, normalizing the microclimate to a given temperature will become an impossible task for the air conditioner and will damage the equipment.
There are two possible scenarios:
- low productivity – operation of the unit is at the limit of its capabilities;
- excess capacity – an increase in the number of on/off switches, which has a detrimental effect on the electric motor.
The ability to heat a room characterizes the heat output of a split. The heat transfer power is always slightly higher than the cooling capacity. The difference between the indicators is the ratio of heat loss along the freon pumping route in cooling and heating modes.
The thermal power indicator is especially relevant if the air conditioner is planned to be used as an interseasonal heating source. A split complex is many times more efficient than an electric heater. About the features of the split system for heat we talked here.

BTU value and labeling explanation
BTU/BTU is a British Thermal Unit for measuring heat energy. The value determines the amount of heat expended to heat one pound of water by 1° Fahrenheit.
It is this unit that expresses the refrigeration capacity of climate control equipment and is often present in product labeling.
Ratio between Watts and BTU/h:
- 1 BTU/h ≈ 0.2931 W, for ease of calculation, 0.3 W is used;
- 1 kW ≈ 3412 BTU/h.
Air conditioning is an American invention that uses Western systems of measurement. For practicality and clarity of display, it was decided to standardize the cooling capacity and express it in round numbers, for example: 7000 BTU/h, 9000 BTU/h, etc.
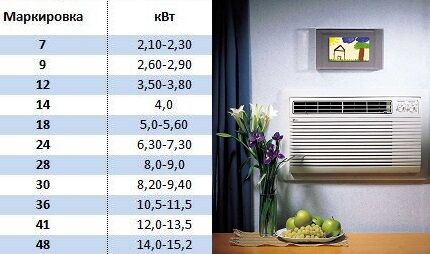
Understanding the digital designation in the equipment labeling, you can approximately determine for which room the air conditioner is designed.
Electricity consumption and energy efficiency assessment
As noted above, in addition to cooling and heating capacity, the power consumption is indicated in the split system passport. The value determines the energy consumption. We recommend that you read the rules calculation of electricity consumption and ways to save it.
However, the coefficient and energy efficiency class are more informative.
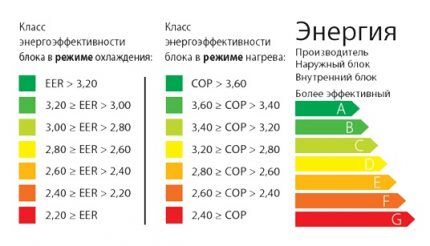
Essentially, the coefficients EER And COP show the amount of cold/heat produced when 1 kW of electrical power is consumed. The higher their numerical value, the higher the efficiency of the climate system and the lower the level of energy consumption.
That is, when EER=2.5 The air conditioner consumes electricity at maximum cooling power Q/2.5. By multiplying the result by the operating period, you can find out the daily energy consumption.
Based on EER, splits are classified into energy efficiency classes. Category “A” includes the most economical units, group “G” represents air conditioners with the highest electricity consumption.

Methods for self-calculation of power
There are several ways to calculate the performance of splits. The simplest, but not reliable enough, is calculation by area. A more accurate method is the thermotechnical method, which takes into account the design features of the room and the total heat inflows.
Option #1 - choosing an air conditioner based on service area
You can determine the approximate power of the unit without mathematical calculations, using a practical assessment criterion - the area of the room.
The average cooling capacity of a split is 1 kW per 10 sq.m of service room. This standard is relevant for residential premises with a ceiling height of 2.5-3 m.
Thus, when calculating the power of the air conditioner, the service area must be divided by 10.For example, for a room of 22 sq.m, a model with a capacity of 2.2 kW is suitable. The resulting value corresponds to “seven” according to the BTU system.
The calculated power is increased by 20% in the following cases:
- location of the room on the sunny side of the house;
- the presence of panoramic windows;
- placement of a large number of office equipment and electrical appliances.
A cooling capacity reserve of 20% must be provided if many people constantly live or work in the room.

Due to the impressive dimensions, possible angularity and curvature, air flows are distributed unevenly. In this case, it is advisable to install multi-system split complexes.
Option #2 - use thermal calculation
Thermal engineering calculations taking into account the design and operational features of the building are considered more accurate. Next, consider the typical formula used for calculations.
Determining factors:
- room dimensions: area and exact height;
- number of people;
- purpose of the premises: gym, active work, recreation, etc.;
- heat sources, household/office equipment;
- the presence of insulated facades and roofs.
The main emphasis in assessing the power of an air conditioner is on the total heat gain.

The greater the heat flow, the higher the cooling capacity of the split should be.
Typical formula:
Q=Q1+Q2+Q3,
Where: Q – final cooling power; Q1 – heat input from the structural elements of the room; Q2 – heat inflows from people; Q3 – heat generation from equipment.
Step #1 - Calculate Q1
The heat excess of a room is determined as follows:
Q1=V*g,
Where: V – the volume of the serviced premises, calculated by multiplying the square footage and the height of the ceilings; g – calculated heat transfer coefficient.
The value of the g indicator depends on the orientation of the windows and the level of natural light in the room:
- 40 – sunny side, intense insolation is typical for southern, southwestern, southeastern orientation;
- 35 – moderate illumination on the eastern, northwestern, western side;
- 30 – the predominance of shading during the day is observed in rooms whose windows face north or northeast.
As you can see, the sunny side will have the highest heat transfer coefficient.
Step #2 - Define Q2
The heat production of people depends on their age and mobility.
The following heat release indicators are typical for an adult:
- rest state – 80 W;
- light work, moderate loads – 125 W;
- vigorous activity – 170 W.
When performing hard work and intense sports exercises, heat production reaches 250 W.

However, this approach is justified when choosing a split system for children's institutions. The air conditioner is purchased for the future, so for a family, the heat transfer of children should be equated to “adult” indicators.
For an apartment cooling system, parameter Q2 is determined by the product of the number of residents and the average heat release value - about 110 W.
Step #3 - Calculate Q3
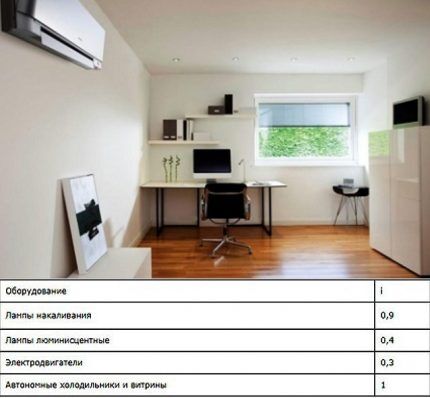
Excess heat from electrical equipment is calculated using the formula:
Q3=N*m*i,
Where:
- N – power of a unit of equipment;
- m — number of household appliances;
- i – coefficient of conversion of electricity into heat.
In the calculations, it is necessary to take into account the frequency of use of equipment during the day, taking round-the-clock work as a unit.
By summing up the total amount of heat inflow, you can determine the power of the air conditioner. It is permissible to exceed the cooling capacity of the unit by 15% of the calculated value or reduce it by a maximum of 5%.
Step-by-step calculations of equipment power
First, let's calculate the required equipment power for a specific room with an area of 24 sq.m. And then we’ll look at the situations in which adjustments are used.
Power calculation for a specific room
Calculation data for determining split performance:
- room area – 24 sq.m, ceiling height – 2.8 cm;
- a room with a standard window facing south;
- number of residents – 2 people;
- equipment: computer, TV, refrigerator (0.3 kW), incandescent lamp (0.1 kW).
Simultaneous operation of the listed electrical appliances is possible.
Step 1 — determination of heat gains from windows, floors, walls and ceilings.
Q1=24*2.7*40=2592 W
The resulting value can be safely rounded to 2.6 kW. The calculation uses the coefficient g=40, since the room is well lit.
Step 2 — calculation of heat gain from people.Let us take the heat production of an adult to be 110 W.
Q2=2*110=220 W or 0.22 kW
Step 3 — heat inflows from equipment are calculated for each type of equipment, taking into account the electricity conversion coefficient:
- computer – 0.3 kW;
- TV – 0.2 kW;
- electric lamp – 90 W (100 W*0.9);
- refrigerator – 100 W (300 W*0.3).
Q3=300+200+90+100=600 W or 0.6 kW
Step 4 — calculation of the cooling capacity of the air conditioner.
Q=2.6+0.22+0.6=3.42 kW
For comparison, it is possible to make an approximate selection of an air conditioner solely by area without taking into account the number of residents and heat inflows. For an area of 24 sq.m., the estimated cooling capacity should be 2.4 kW, taking into account good lighting - 2.4 * 1.2 = 2.88 kW.

In this situation, the calculation results using the two methods differ. The priority is “thermal” calculation. The cooling power of the air conditioner must extinguish all possible heat gains.
Taking into account special operating conditions
The method described above in most cases does not need adjustment and gives an accurate result.
Deserves special attention:
- the need for regular ventilation;
- location of the room on the top floor;
- hot climate of the region;
- large glazing area.
Let's consider all these cases in more detail.
Fresh air supply
The documentation for split systems usually stipulates that operating the device with open windows is undesirable.

To maintain a normal microclimate without constantly moving the sash, you can leave the window with micro-ventilation or install supply valve. Both options do not provoke drafts when the front door is closed.
When operating the split in conditions of gentle ventilation, the following should be taken into account:
- In order to compensate for the additional heat load, the Q1 indicator when calculating the power of the air conditioner must be increased by 20%.
- Electricity consumption during split operation will increase to 15%.
In hot weather, do not rely on power reserves. If there is significant heat inflow, the air conditioner will not provide the set temperature.
Top floor of living space
In attics and apartments on the top floors without an attic, the heat of the heated roof is transferred into the room. The situation is aggravated with dark-colored flat roofs.

Hot climate of the region
One of the rules for safe use of an air conditioner is to maintain the permissible temperature difference between the outside and inside the building. The limit value is 10 °C. For example, if it is 35 °C outside the window, then the recommended room temperature is not lower than 25 °C.
The rated power of split complexes is indicated taking into account operation in conditions up to 31-33 °C.When the indicator increases to 40 °C or more, the cooling capacity of the unit is not enough to maintain the coveted 18-20 °C.
Taking into account the climate's predisposition to hot summers and one's own preferences for the level of coolness, when calculating, the Q1 indicator should be additionally increased by 20-30%.
Large windows in the room
The standard formula assumes that there is one window in the room of standard dimensions - up to 2 sq.m. Several window openings or a panoramic design increases unaccounted heat gain.

The cooling power is adjusted based on each square meter of additional glazing:
- + 200-300 W – for the sunny side;
- + 100-200 W – moderate insolation of the room;
- + 50-100 W – predominance of shading.
Light-colored blinds or curtains will help reduce solar heat gain.
Additional criteria for choosing an air conditioner
In addition to the power characteristics of the system and energy efficiency class, before purchasing, you should decide on the following parameters:
- type of air conditioner;
- operating principle of the unit;
- functionality;
- by the manufacturer.
Next, we will consider each of these criteria in more detail.
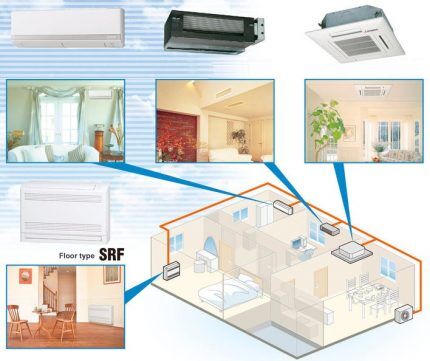
Criterion #1 - type of air conditioner
For domestic use, monoblocks and split systems. The first category includes window models and compact portable devices. Window-mounted air conditioners have lost their former popularity.

The undeniable advantages of window “coolers”: low cost and maintainability. This unit is more suitable for seasonal country use than for an apartment.
Mobile monoblocks are equipped with a flexible air duct that removes heat to the street. A portable air conditioner is the optimal solution for a rented space. We have given the rating of the best mobile models In this article.

Split systems confidently occupy a leading position among household air conditioning systems.
Based on the form of execution, there are two categories of splits:
- Double block design. A pair of modules are connected by a closed freon line. The complex is easy to operate and almost silent. Various design options for the indoor unit are available; the housing does not take up useful space in the room.
- Multi-system. The external module ensures the operation of two to five internal units.
The use of a multi-complex allows you to set different air conditioning parameters in individual rooms.
Criterion #2 - operating principle
There are conventional and inverter models.
The operating procedure of a traditional split system:
- When the temperature rises, the air conditioner turns on.
- After cooling to the designated limit, the unit turns off.
- The on/off duty cycle is repeated continuously.
And here inverter air conditioner operates more smoothly. After startup, the room is cooled, but the device continues to operate at reduced power, maintaining the desired temperature.
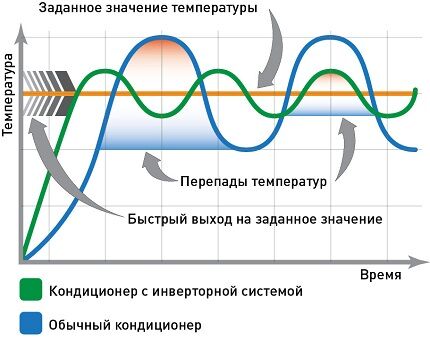
Due to the absence of “sharp” cyclical operation, inverter air conditioners are low noise and durable.
You don't know either what is better to choose — inverter or conventional air conditioner? In this case, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with their main differences, as well as the pros and cons of each option.
Criterion #3 - features and brand
Manufacturers, in an effort to win the favor of customers, equip split systems with additional options.
It’s good if the air conditioner has the following functions:
- fan distribution of air flow;
- automatic restoration of device settings;
- remote control;
- built-in timer.
Another popular air conditioner function among users is fresh air supply. Many manufacturers offer such models.

The equipment manufacturer plays a significant role in the choice - the better the brand reputation, the higher the quality indicators and reliability of the equipment.
The ranking of leading manufacturers is dominated by foreign companies: Daikin, LG, Sharp, Hitachi, Panasonic and General Climat. We reviewed the best air conditioner models in the next article.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Practical recommendations from a specialist will help you determine the power characteristics of the air conditioner:
Understanding the principles of calculating the performance of air conditioning systems, you will be able to independently determine the range of permissible power.
It is better to entrust the final calculation of suitable parameters to professionals - an experienced specialist will take into account all operational nuances and select the optimal air conditioner model.
Do you need an air conditioner, but you don’t want to make a mistake with the power and choose insufficiently efficient equipment for your apartment/house? Maybe you still have questions about the calculations or want to clarify certain nuances? Ask for advice in the comments - our experts and competent site visitors will try to clarify all the points.




I always dreamed of purchasing an air conditioner for my home, but I was worried that I wouldn’t be able to regulate the comfortable air temperature well enough and risked getting a serious cold. But then I found out that this does not depend on the temperature, but on insufficient care of the equipment, which results in the formation of a good environment for the development of harmful bacteria. This device is a great help in the summer, when there is high humidity outside and the stuffiness is unbearable. In order for the air conditioner to last a long time and without health consequences, it is necessary to carry out regular cleaning, at least once a month. I would like the author to complement and give detailed recommendations regarding cleaning the air conditioner; this is very important information.
There is such an article, Valentina, on the website - you can study it: “Do-it-yourself cleaning of split systems: preventive inspection and care of equipment».
Some do not recognize the usefulness of air conditioning and suffer from the heat, saving themselves with a regular fan, but in vain. As soon as you turn it off, it gets even worse. That’s why they came up with an air conditioner, and several types were specially developed. We have an inverter option, it is really silent, maintains a comfortable temperature and is easy to use. By choosing the right power, you can save a lot of energy. Don't skimp on comfort.
Wow, what subtle calculations for selection. Today, for the first time, I heard that when choosing an air conditioner, you need to calculate something. This information will be especially relevant for sellers of these same splits, since in most cases they sell simply: “What is your area? We have 25 sq.m., well then this model is ideal for you.” ))))
Well, sellers in chain stores are guided by the simplest formula - 1 kW of power per 10 sq.m. Yes, it works, but for apartments up to 60 sq.m. In general, it is not the seller who should be involved in calculating the power of an air conditioner or split system. It is very rare for a consultant in an electronics hypermarket to have a good understanding of air conditioners, washing machines, computers, and other things at the same time.
For a one-room apartment, one air conditioner will be enough, calculated based on the service area. And for a two-room apartment or more, as well as for a private house, it is better to use thermal calculations. Here, no consultant in the store will help, you need to attract a specialist and pay money for the work. In this case, a multi-split system is the optimal solution.
Manufacturers of air conditioners, Alexander, are guided by the average dimensions of apartments, replacing the volume with “square meters”. The average American ceiling, for example, is 2.4 meters, and the Japanese one is 2.1. Old Russian apartments had a height of 2.6 meters, modern ones - 2.4. However, they promise to bring it to 2.8. As you can see, the spread from the global average height is small, but the increase in volume can be critical for the air conditioner.
Good afternoon. 1 sq. Room 22 sq.m. Height 2.75. Not the last floor. The windows are standard. One person, PC, TV. West side, sun after 12 noon. I calculated the heat inflows using the formula - 2.8 kW. The question arose - 9ksha that is a little short or 12ksha that is overlapping?
Are heating batteries deliberately ignored in some calculations?